QCheckBox
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# A QCheckBox is an option button that can be
# checked, unchecked or partially checked.
import sys
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot, Qt
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QApplication,
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QCheckBox, QLabel)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.resize(300, 200)
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# 1 - Create the checkboxes and add them to the layout
self.windows_checkbox = QCheckBox('Windows')
self.windows_checkbox.setObjectName('Windows')
self.linux_checkbox = QCheckBox('Linux')
self.linux_checkbox.setObjectName('Linux')
self.macos_checkbox = QCheckBox('macOS')
self.macos_checkbox.setObjectName('macOS')
self.macos_checkbox.setTristate(True)
self.label = QLabel()
layout.addWidget(self.windows_checkbox)
layout.addWidget(self.linux_checkbox)
layout.addWidget(self.macos_checkbox)
layout.addWidget(self.label)
# 3 - For each checkbox connect QCheckBox.checkStateChanged signal
# with the slot. checkStateChanged is emitted when a checkbox
# state changes.
self.windows_checkbox.checkStateChanged.connect(self.on_state_changed)
self.linux_checkbox.checkStateChanged.connect(self.on_state_changed)
self.macos_checkbox.checkStateChanged.connect(self.on_state_changed)
# 2 - Create the slot. Mark it with the @Slot() decorator
# If you don't import PySide6.QtCore.Qt above
# PySide6 will complain: TypeError: Cannot call meta function ...
@Slot()
def on_state_changed(self, state):
sender_name = self.sender().objectName()
self.label.setText(f'{sender_name} {state}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = Window()
main_window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
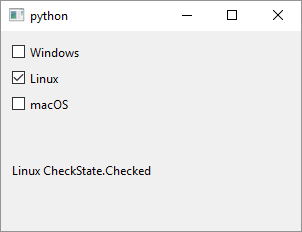
QCheckBox is a widget that has a graphical check box and a label. it can be checked, unchecked and, if you set its tristate property to True, partially checked. Checkboxes are commonly used to represent options that are not mutually exclusive - more than one checkbox in a group can be checked at the same time. To use QCheckBox in your application
-
Create a
QCheckBoxobject passing the text to be displayed to the constructor. In the example we create three checkboxes, one for each popular operating system and add each of them to the window’s layout. We also set each checkboxobjectNameproperty. SettingobjectNamecan be useful in debugging or when you need to find a widget usingQObject.findChild()asobjectNameis initially empty. -
Create the slot to process checkboxes’
checkStateChangedsignals. The documentation suggests that you mark it with theSlot()decorator but if you do you also need to import theQtclass fromPySide6.QtCore. If you don’t PySide6 will complain:TypeError: Cannot call meta function “void on_state_changed(Qt::CheckState)” because parameter 0 of type “Qt::CheckState” cannot be converted.
This is because
checkStateChangedstateargument is of typeQt.CheckStateandQt.CheckState, like many other Qt enums, resides inPySide6.QtCore.Qtso you’ll often need to import it. So, in this case, either importQtor omit theSlot()decorator. -
Finally, connect each checkbox’
checkStateChangedsignal to the created slot.