QListWidget
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
# The QListWidget class provides an item-based
# list widget, ie. it displays a list of items.
# This is a basic example. You can also add
# icons and checkboxes. QListView is even more flexible.
import sys
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QApplication,
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QListWidget, QLabel)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# 1 - Create the list widget and add items to it
self.list_widget = QListWidget()
self.list_widget.addItems(['blue', 'green', 'red'])
self.label = QLabel()
layout.addWidget(self.list_widget)
layout.addWidget(self.label)
# 3 - Connect the list widget currentItemChanged signal
# with the slot.
self.list_widget.currentItemChanged.connect(
self.on_current_item_changed)
# 2 - Create the slot to handle item changed events
@Slot()
def on_current_item_changed(self, current, previous):
color = current.text()
self.label.setStyleSheet(
'background-color:{};'.format(color))
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = Window()
main_window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
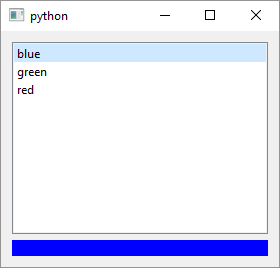
The QListWidget is a widget that displays a list of items. There are two main ways you can add items to a QListWidget: a) by creating a series of QListWidgetItem objects and adding them to your QListWidget using the QListWidget.addItem() method or b) by passing a list of strings to the QListWidget constructor, in which case QListWidget automatically creates a QListWidgetItem for each string in the list. To use QListWidget in your application
-
Create a
QListWidgetinstance and add items to it. In the example we create threeQListWidgetItems and add the to theQListWidgetbut there are also twoaddItems()methods that allow you to add a list ofQListWidgetItems or strings. We also create aQLabelinstance whose background color will change whenQListWidgetcurrent item changes. -
Create a slot to handle the
QListWidget.currentItemChangedsignals.currentItemChangedhas two arguments,currentandpreviousand we usecurrentto get the currently selected item text and set theQLabel’s style sheet accordingly. -
Connect the signal and the slot. In addition to the
currentItemChanged,QListWidgetprovides several other signals related to its item manipulation.
This is a basic example of QListWidget usage. In addition to the above, you can add icons and checkboxes to items or make them editable. QListWidget’s parent class, QListView is part of the Qt model/view framework which makes it even more flexible.