QToolBox
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# The QToolBox class provides a column of tabbed widget items
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QApplication,
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QToolBox, QPushButton, QLabel)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# 1 - Create the toolbox
toolbox = QToolBox()
# 2 - Create the widgets (buttons in this case)
windows_button = QPushButton('Windows')
mac_button = QPushButton('Mac')
linux_widget = QWidget()
linux_widget.setLayout(QVBoxLayout())
debian_button = QPushButton('Debian')
arch_button = QPushButton('Arch')
linux_widget.layout().addWidget(debian_button)
linux_widget.layout().addWidget(arch_button)
# 3 - Add widgets to the toolbox
toolbox.addItem(windows_button, 'Win')
toolbox.addItem(mac_button, 'Mac')
toolbox.addItem(linux_widget, 'Lin')
windows_button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked)
mac_button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked)
debian_button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked)
arch_button.clicked.connect(self.on_clicked)
self.label = QLabel()
layout.addWidget(toolbox)
layout.addWidget(self.label)
def on_clicked(self):
self.label.setText(self.sender().text() + ' clicked!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = Window()
main_window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
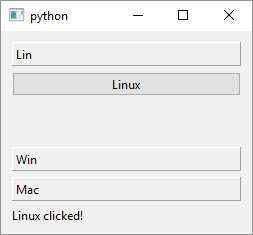
QToolBox provides a column of tabbed widget items. This doesn’t really tell you much - it is a Qt container widget pretty similar to the ubiquitous accordion widget that lets you pack multiple widgets within a relatively small space and expand or collapse them as needed. QToolBox pages are called items in the documentation. To use QToolBox in your application
-
Create a
QToolBoxobject -
Create the child widgets. In the example we simply create three push buttons each representing a popular operating system. You can also add multiple child widgets to a page by adding them to a layout as demonstrated on the `Linux’ page.
-
Add the widgets to the toolbox using
QToolBox.addItem()
In the example we also handle the child push buttons clicked signals for demonstration purposes, setting a label’s text to the text of the clicked button.