QScrollArea
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# The QScrollArea class provides a
# scrolling view onto another widget
import sys
from PySide6.QtGui import QTextOption
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QApplication,
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QScrollArea, QPlainTextEdit)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# 1 - Create the scroll area
scroll_area = QScrollArea()
# 2 - Create the widget that needs to be scrolled
text_edit = QPlainTextEdit()
text_edit.setWordWrapMode(QTextOption.WrapMode.NoWrap)
# 3 - Add the widget to the scroll area
scroll_area.setWidget(text_edit)
# Use this if you want the inner widget to
# get resized together with the scroll area.
scroll_area.setWidgetResizable(True)
layout.addWidget(scroll_area)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = Window()
main_window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
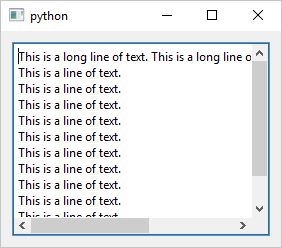
If a QScrollArea’ child widget exceeds its size it provides scrollbars so that the whole child widget can be viewed. To use it in your application
-
Create a
QScrollAreaobject -
Create the child widget. In the example we use a
QPlainTextEditobject and set its wrap mode toWrapMode.NoWrapso that it expands when text is entered -
Add the
QPlainTextEditto the scroll area usingQScrollArea.addWidget(). We also set theQScrollArea.widgetResizableproperty toTrueso that the text box resizes along with the scroll area.
Now if you enter a long line of text in the text box the scroll area shows the horizontal scrollbar and if you enter several lines the scroll area shows the vertical scrollbar.