QSpinBox and QDial
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# The QSpinBox class provides a spin box widget.
# The QDial class provides a rounded range control
# (like a speedometer or potentiometer).
#
# Access their current value using their value() property
import sys
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QApplication,
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QSpinBox, QDial, QLabel)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# 1 - Create the widgets
self.spinbox = QSpinBox()
self.spinbox.setRange(0, 100)
self.spinbox.setSingleStep(5)
self.dial = QDial()
self.dial.setRange(0, 100)
self.label = QLabel()
# 3. Connect the signals with the slot functions
self.spinbox.valueChanged.connect(
self.on_spinbox_value_changed)
self.dial.valueChanged.connect(
self.on_dial_value_changed)
layout.addWidget(self.spinbox)
layout.addWidget(self.dial)
layout.addWidget(self.label)
# 2. Write the slots. The value passed
# from the signals is an integer.
@Slot()
def on_spinbox_value_changed(self, i):
self.dial.setValue(i)
self.label.setText(str(i))
@Slot()
def on_dial_value_changed(self, i):
self.spinbox.setValue(i)
self.label.setText(str(i))
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = Window()
main_window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
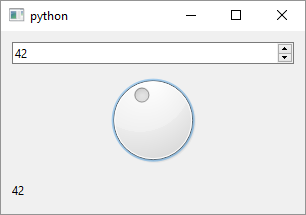
QSpinBox provides a spin box widget with up and down arrows and QDial is a rounded range widget visually similar to a potentiometer. While both widgets provide similar functionality, ie. let the user select an integer from a range of values they do not inherit each other. Here is what their inheritance tree looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
QWidget
...
QAbstractSlider
QDial
QScrollBar
QSlider
...
QAbstractSpinBox
QDateTimeEdit
QDateEdit
QTimeEdit
QDoubleSpinBox
QSpinBox
...
QSpinBox parent class is QAbstractSpinBox while QDial parent is QAbstractSlider and their common ancestor is QWidget, shared with all the Qt widget classes. To use QSpinBox and QDial in your application
-
Create the widgets and set their value range. In the example the range is between 0 and 100 for both widget objects. The example also has a
QLabelthat echoes the current value. -
Write the slot methods. Both widgets’
valueChanged()signals passes an integer value to slots so if you want to use it to set a label’s text you first need to convert it to a string. -
Connect the widgets’
valueChanged()signals to the slots.