QTreeWidget
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
# The QTreeWidget class provides a standard tree widget.
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QApplication,
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QTreeWidget,
QTreeWidgetItem, QLabel)
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# 1 - Create the tree widget
self.tree_widget = QTreeWidget()
# 2 - Create the tree widget items and add them
# to the tree widget
#
# apes parent is self.tree_widget which means
# apes is the root item
#
# ['Apes'] is the item text. It's a list with one element.
# That's because a tree widget has one column by default.
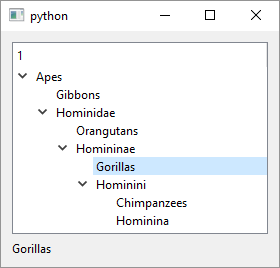
apes = QTreeWidgetItem(self.tree_widget, ['Apes'])
# Add other items to the tree. The pattern is the same
# as for the root item: (parent, text)
# There are several other QTreeWidgetItem
# constructors as well.
gibbons = QTreeWidgetItem(apes, ['Gibbons'])
hominidae = QTreeWidgetItem(apes, ['Hominidae'])
ponginae = QTreeWidgetItem(hominidae, ['Orangutans'])
homininae = QTreeWidgetItem(hominidae, ['Homininae'])
gorillinae = QTreeWidgetItem(homininae, ['Gorillas'])
hominini = QTreeWidgetItem(homininae, ['Hominini'])
panina = QTreeWidgetItem(hominini, ['Chimpanzees'])
hominina = QTreeWidgetItem(hominini, ['Hominina'])
# Add some event handling just for show.
self.tree_widget.currentItemChanged.connect(
self.on_current_item_changed)
self.label = QLabel()
# 3 - Add the tree widget to the layout
layout.addWidget(self.tree_widget)
layout.addWidget(self.label)
# The label will display currently selected item text.
def on_current_item_changed(self, current, previous):
self.label.setText(current.text(0))
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = Window()
main_window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
The QTreeWidget provides a standard tree widget. It uses a predefined item model - each tree node is represented with a QTreeWidgetItem instance. To use `QTreeWidget in your application
-
Create a
QTreeWidgetobject. It has only one constructor that optionally accepts the tree widget’s parent widget but we don’t set it here because adding a widget to a layout automatically sets the widget’s parent. -
Create
QTreeWidgetItemobjects and add them to the tree widget. Each tree node is represented by aQTreeWidgetItemobject. If you set theQTreeWidgetas its parent, like we do with theapesQTreeWidgetItemit becomes a root/top level item. If you set anotherQTreeWidgetItemas the parent that item becomes the parent and you use this parent-child relationship to form a tree structure that is displayed it the tree widget. We also use string lists like['Gibbons']to set the text to be displayed for eachQTreeWidgetItem.QTreeWidgethas one column by default but you can add more if you need. -
Add necessary slots, connect them with the appropriate
QTreeWidgetsignals and add the tree widget to the window layout. In the example we set a label’s text to the current item text each time the tree widget current item changes.